Case Series/Study
(CS-067) Application of topical dessicanting agent in dehiscent complex wounds after cardiac surgery
Thursday, May 16, 2024
7:30 PM - 8:30 PM East Coast USA Time
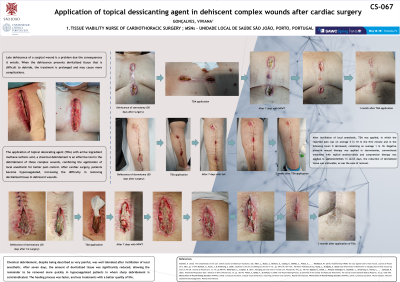
Introduction: Late dehiscence of a surgical wound is a problem due to the consequences it entails. When the dehiscence presents devitalized tissue that is difficult to debride, the treatment is prolonged and may cause more complications. The application of topical desiccating agent (TDA) with active ingredient methane sulfonic acid, a chemical debridement is an effective tool in the debridement of these complex wounds, combining the application of local anesthetic for better pain control.
Methods: Series of cases of application of TDA in dehiscence of three sternotomies and three saphenectomies with more than 30 days after surgery, with devitalized tissue that is difficult to remove, in hypocoagulated patients, with local anesthetic instilled in the wound bed.
Results: After instillation of local anesthetic, TDA was applied, in which the reported pain was on average 5 in 10 in the first minute and in the following hours it decreased, remaining on average 1 in 10. Negative pressure wound therapy was applied in sternotomies, conventional treatment with topical antimicrobials and compression therapy was applied in saphenectomies. In seven days, the reduction of devitalized tissue was noticeable, as was the ease of removal.
Discussion: Chemical debridement, despite being described as very painful, was well tolerated after instillation of local anesthetic. After seven days, the amount of devitalized tissue was significantly reduced, allowing the remainder to be removed more quickly in hypocoagulated patients in whom sharp debridement is contraindicated. The healing process was faster, and less treatments required with a better quality of life.
Methods: Series of cases of application of TDA in dehiscence of three sternotomies and three saphenectomies with more than 30 days after surgery, with devitalized tissue that is difficult to remove, in hypocoagulated patients, with local anesthetic instilled in the wound bed.
Results: After instillation of local anesthetic, TDA was applied, in which the reported pain was on average 5 in 10 in the first minute and in the following hours it decreased, remaining on average 1 in 10. Negative pressure wound therapy was applied in sternotomies, conventional treatment with topical antimicrobials and compression therapy was applied in saphenectomies. In seven days, the reduction of devitalized tissue was noticeable, as was the ease of removal.
Discussion: Chemical debridement, despite being described as very painful, was well tolerated after instillation of local anesthetic. After seven days, the amount of devitalized tissue was significantly reduced, allowing the remainder to be removed more quickly in hypocoagulated patients in whom sharp debridement is contraindicated. The healing process was faster, and less treatments required with a better quality of life.

.jpeg)