Case Series/Study
(CS-130) Enhancement of Wound STO2 with Best Practice TIMERS Methodology and Utilization of Cellular, Acellular and Matrix-Like Products (CAMPs)
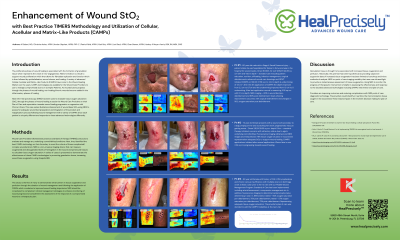
The proliferative phase of wound healing is associated with the formation of granulation tissue which represents the onset of neo-angiogenesis. Matrix formation is critical to support wound proliferation which then allows for fibroblast replication and function which is then followed by epithelialization, wound closure, and healing. A variety of advanced Cellular, Acellular and Matrix-Like Products (CAMPs) have come to the Wound Healing Market over the years. CAMPs technologies are available for the Wound Care Providers to use to manage compromised ulcers on Complex Patients. As wounds/ulcers progress through the phases of wound healing; non-healing/chronic wounds become stalled in the inflammatory phases of healing.
Methods:
Wound Care Providers followed best practices standard of therapy (TIMERS) protocols to evaluate and manage any underlying co-morbidities/conditions. Next, they identified the best CAMPs technology on their formulary to meet the criteria of these complicated/complex wounds/ulcers. NIRS (SnapshotNIR). NIRS is a non-invasive imaging device that can measure oxygenated and de-oxygenated levels of hemoglobin in the wound and peri-wound tissues to calculate tissue oxygen saturation. A series of cases is presented to demonstrate the effectiveness of these CAMPs technologies in promoting granulation tissue, increasing wound base oxygenation using SnapshotNIR.
Results:
This study is the first of many to demonstrate enhancement in tissue oxygenation and perfusion through the duration of wound management and following the application of CAMPs which correlates to improved wound healing trajectories. NIRS should be considered to complement clinical management strategies to enhance monitoring of wound progress and complement the assessment of the response of a compromised wound to a therapeutic plan.
Discussion:
Granulation tissue is thought to be associated with increased tissue oxygenation and perfusion. Historically, this premise has been hypothetical as providing subjective supportive data of increased tissue oxygenation has been limited to benchtop and invitro methods of analysis. NIRS is a point of care imaging modality, that uses near infrared light to provide an instantaneous assessment of tissue oxygenation. Using NIRS to monitor the progress of therapeutic intervention is helpful in assessing the effectiveness and response to the decided advanced technologies including CAMPs intervention and plan of care.

.jpeg)