Case Series/Study
(CS-162) 24 Month Retrospective Review of Pilonial Disease Plastic Surgical Excision and Reconstruction Techniques involving the use of Pure Hypochlorous Acid (pHA) Preserved Wound Solution for Wound Bed Preparation.
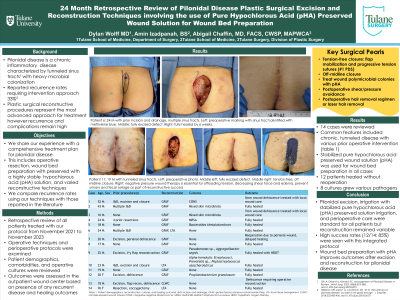
Pilondial disease complicated by chronic inflammatory, fibrotic, and tunneled features represent a difficult clinical challenge. These wounds are often refractory to medical and surgical management and have underlying heavy microbial colonization. Plastic surgical reconstructive procedures represent the most advanced approach. However, the rate of recurrence and complications after surgery remains high. We share our experience with a comprehensive treatment plan including operative resection, wound preparation with pure hypochlorous acid (pHA) preserved solution and varied reconstructive surgical techniques, which have led to low recurrence and high surgical success rates.
Methods: Data was collected by retrospective review of all patients with pilonidal disease treated with surgical excision and plastic surgical complex closure and flap techniques at one academic hospital from November 2021 to November 2023. 14 patients were recognized by these criteria with 14 operative episodes. Operative techniques and perioperative protocols were examined. In addition, patients’ demographics, comorbidities, and operative cultures were reviewed. Outcomes were assessed in the outpatient wound center based on presence of any recurrent disease and healing outcomes of the surgical sites.
Results:
14 patients with pilonidal disease requiring surgical excision and plastic surgical wound closure were examined. Common features included chronic, tunneled disease with various prior operative intervention (table 1.) Pure hypochlorous acid (pHA) preserved solution irrigation was used before wound closure in all cases The most common reconstructive techniques were local advancement flaps (myocutaneous and fasciocutaneous), adjacent tissue transfer, and skin substitute graft. 2 patients underwent reoperation for wound dehiscence. 12 patients healed from their pilonidal disease excision and reconstruction without reoperation. 2 patients had minor (5%) wound dehiscence treated with local wound care. Cultures were sent from 11 patients with 6 cultures growing various pathogens (table 1.)
Discussion: Pilonidal disease excision, irrigation with pure hypochlorous acid (pHA) preserved solution irrigation, and perioperative care were standard for all patients but reconstructive procedure selection remained variable. High surgical success rates were seen with this integrated protocol. Wound bed preparation with pHA is an effective technique for improving outcomes after plastic surgical excision pilonidal disease and reconstruction.

.jpeg)