Case Series/Study
(CS-091) Application of a Novel Meshed Human Reticular Acellular Dermal Matrix* Supports Lower Extremity Wound Closure
Thursday, May 16, 2024
7:30 PM - 8:30 PM East Coast USA Time
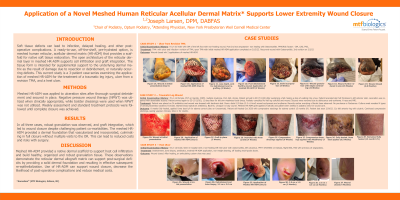
Introduction: Soft tissue defects can lead to infection, delayed healing, and other post-operative complications. A ready-to-use, off-the-shelf, pre-hydrated option, is meshed human reticular, acellular dermal matrix (HR-ADM) that provides a scaffold for native soft tissue restoration. The open architecture of the reticular dermal layer in meshed HR-ADM supports cell infiltration and graft integration. The tissue form is intended for supplemental support to the underlying dermal matrix as the result of damage due to resection or debridement, or naturally occurring defects. This current study is a 3-patient case-series examining the application of meshed HR-ADM for the treatment of a traumatic leg injury, ulcer from a revision TMA, and a heel ulcer.
Methods: Meshed HR-ADM was applied to ulceration sites after thorough surgical debridement and secured in place. Negative pressure wound therapy (NPWT) was utilized when clinically appropriate, while bolster dressings were used when NPWT was not utilized. Weekly assessment and standard treatment protocols were followed until complete closure was achieved.
Results: In all three cases, robust granulation was observed, and graft integration, which led to wound closure despite challenging patient co-morbidities. The meshed HR-ADM provided a dermal foundation that vascularized and incorporated, culminating in full closure without multiple visits to the OR. This can lead to reduced costs and risks with surgery.
Discussion: Meshed HR-ADM provided a native dermal scaffold to support host cell infiltration and build healthy, organized and robust granulation tissue. These observations demonstrate the reticular dermal allograft matrix can support post-surgical deficits by providing a solid dermal foundation and resulting in effective subsequent re-epithelialization. Use of HR-ADM can support wound closure, decrease the likelihood of post-operative complications and reduce medical costs.
Methods: Meshed HR-ADM was applied to ulceration sites after thorough surgical debridement and secured in place. Negative pressure wound therapy (NPWT) was utilized when clinically appropriate, while bolster dressings were used when NPWT was not utilized. Weekly assessment and standard treatment protocols were followed until complete closure was achieved.
Results: In all three cases, robust granulation was observed, and graft integration, which led to wound closure despite challenging patient co-morbidities. The meshed HR-ADM provided a dermal foundation that vascularized and incorporated, culminating in full closure without multiple visits to the OR. This can lead to reduced costs and risks with surgery.
Discussion: Meshed HR-ADM provided a native dermal scaffold to support host cell infiltration and build healthy, organized and robust granulation tissue. These observations demonstrate the reticular dermal allograft matrix can support post-surgical deficits by providing a solid dermal foundation and resulting in effective subsequent re-epithelialization. Use of HR-ADM can support wound closure, decrease the likelihood of post-operative complications and reduce medical costs.

.jpeg)